This article will cover the step-by-step process of installing Docker on an Ubuntu Server.
Step 1. Update the apt package index.
sudo apt update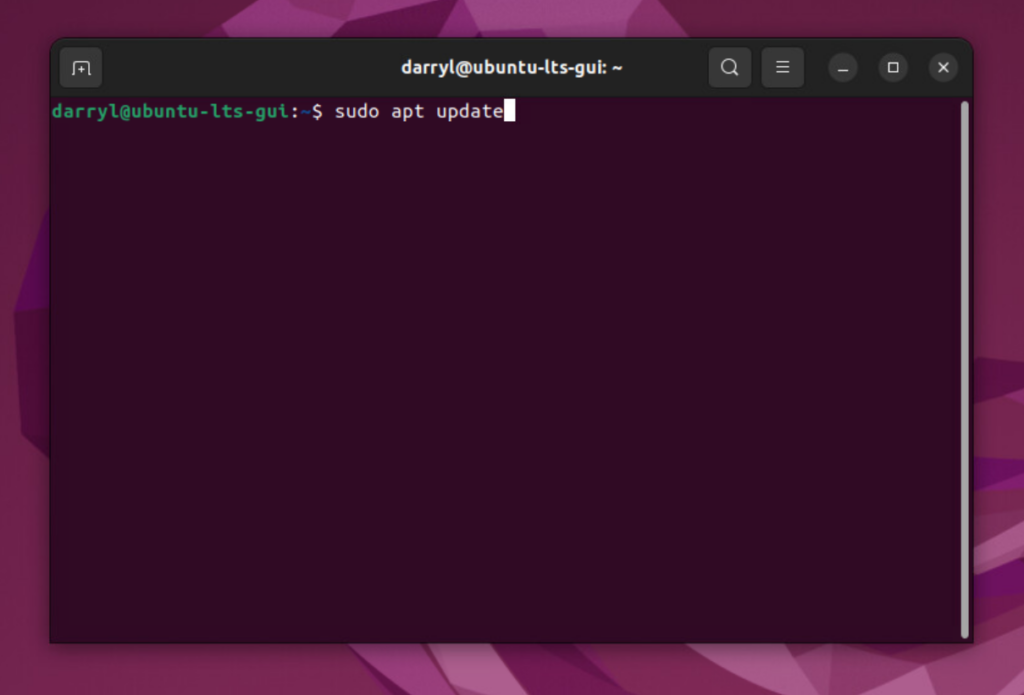
Step 2. Install packages that allow us to use the repository over HTTPS.
sudo apt-get install \
ca-certificates \
curl \
gnupg \
lsb-releaseCode language: JavaScript (javascript)Step 3. Adding the official Docker GPG keys
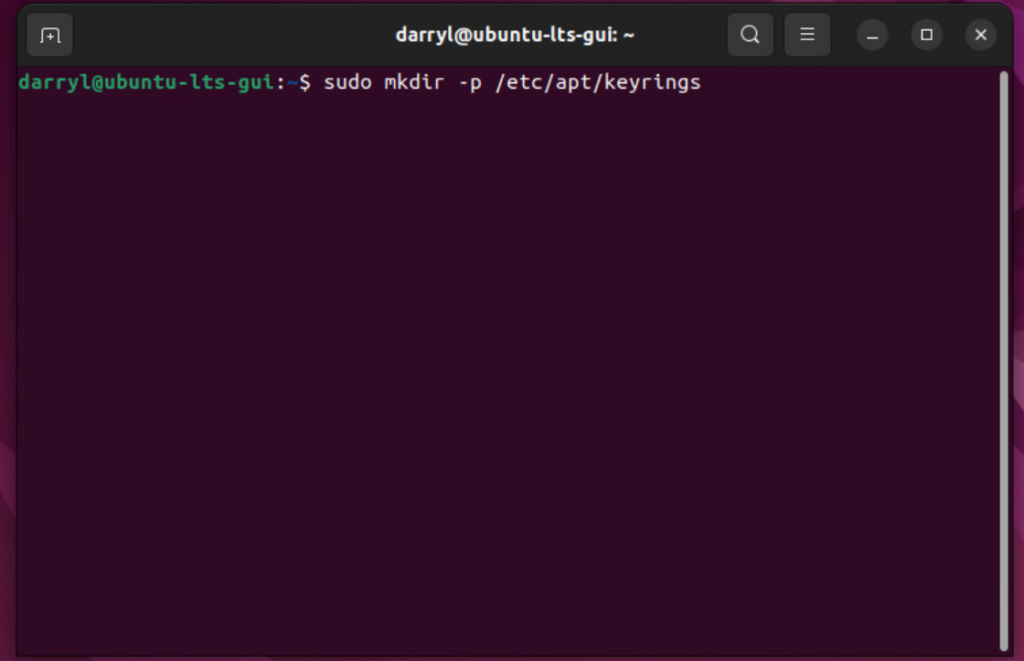
sudo mkdir -p /etc/apt/keyrings
curl -fsSL https://download.docker.com/linux/ubuntu/gpg | sudo gpg --dearmor -o /etc/apt/keyrings/docker.gpgCode language: JavaScript (javascript)Step 4. Adding the Docker repository
echo \
"deb [arch=$(dpkg --print-architecture) signed-by=/etc/apt/keyrings/docker.gpg] https://download.docker.com/linux/ubuntu \
$(lsb_release -cs) stable" | sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/docker.list > /dev/nullCode language: PHP (php)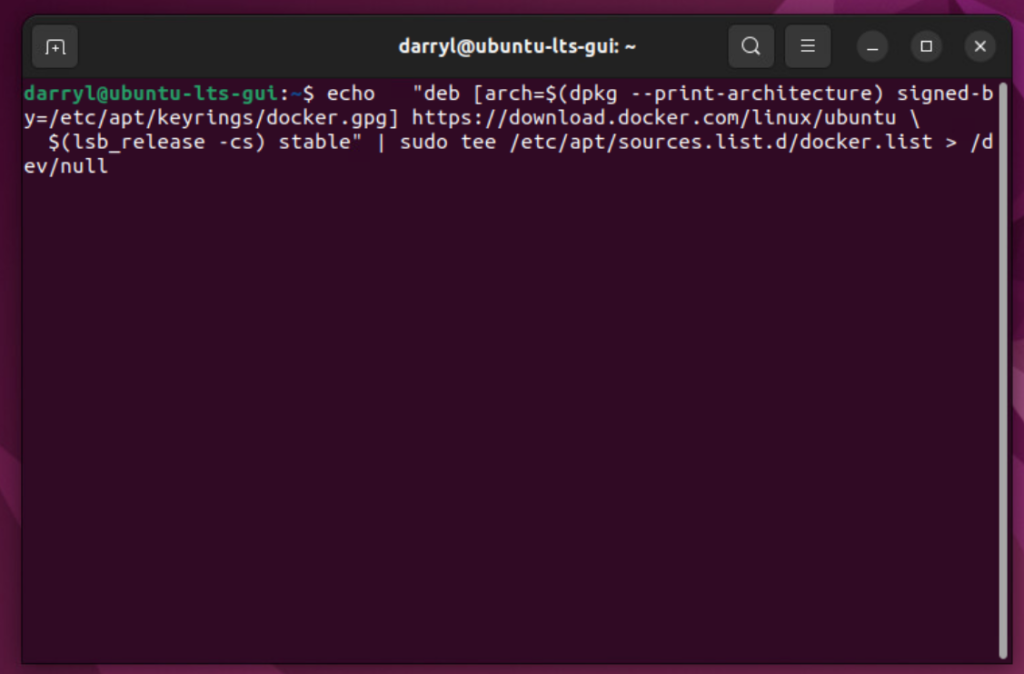
Step 5. Update the apt package index once more, so we have the Docker packages added to the package index.
sudo apt update
Step 6. Install Docker and its components
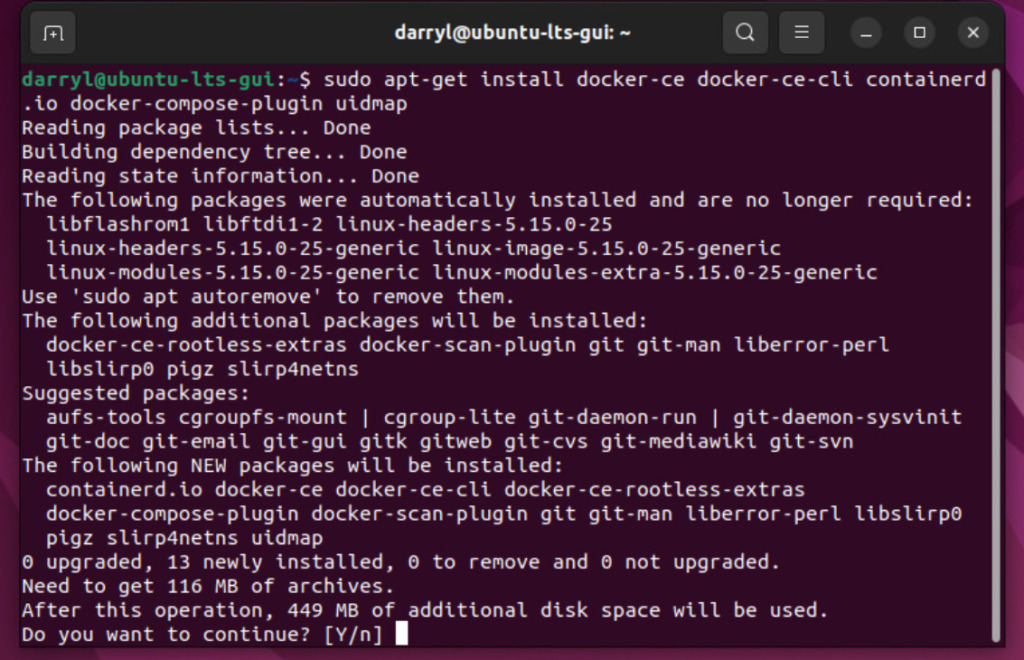
sudo apt-get install docker-ce docker-ce-cli containerd.io docker-compose-plugin uidmapCode language: JavaScript (javascript)
Step 7. Start Docker.
The command below will start Docker.
sudo systemctl start docker
You can also enable Docker to run at startup. It will be useful if you are using it in production.
sudo systemctl enable docker
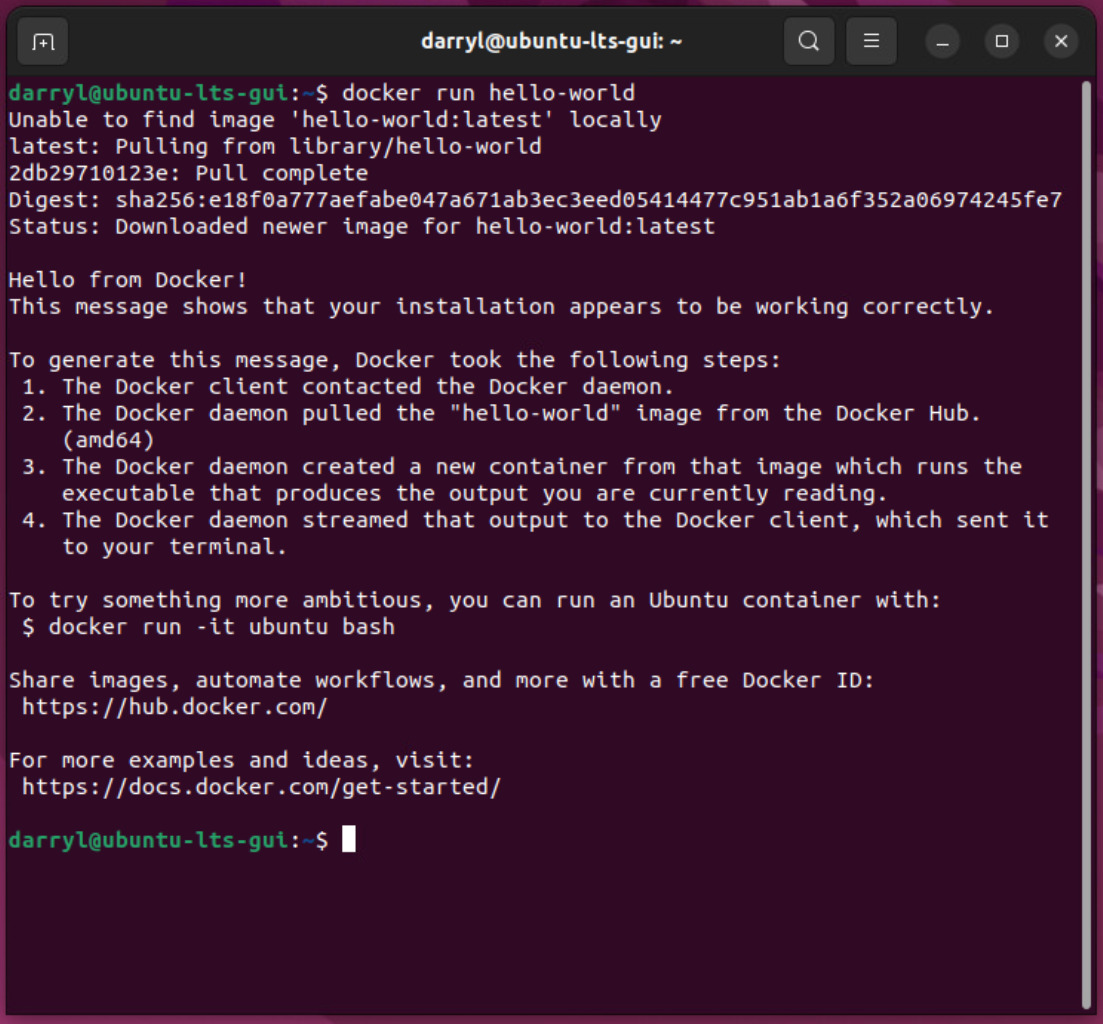
Now that we have Docker installed, we can run the hello-world container.
sudo docker run hello-world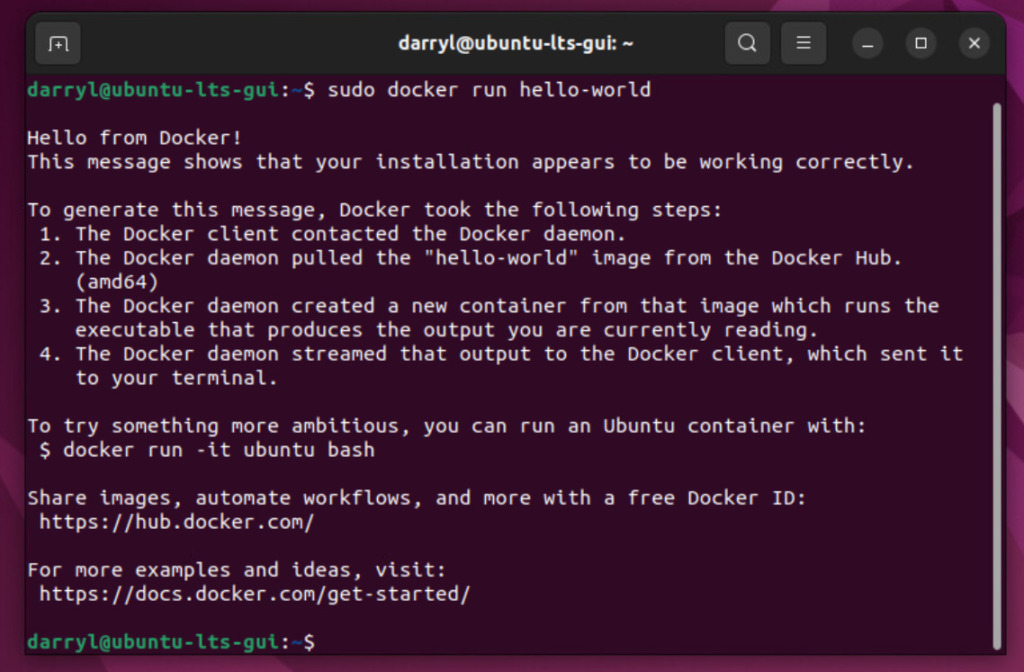
If the above command runs successfully, we can proceed further and set up Docker to execute rootlessly. It means we don’t need to run sudo before the docker command.
dockerd-rootless-setuptool.sh installCode language: CSS (css)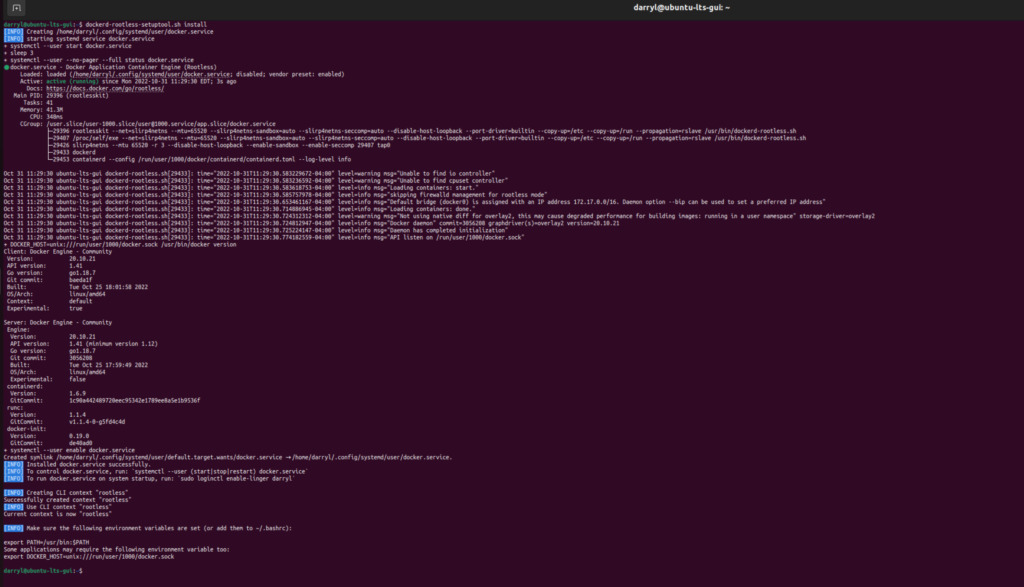
We can now run any docker container rootless, so to test this, let’s rerun the hello-world container.
docker run hello-world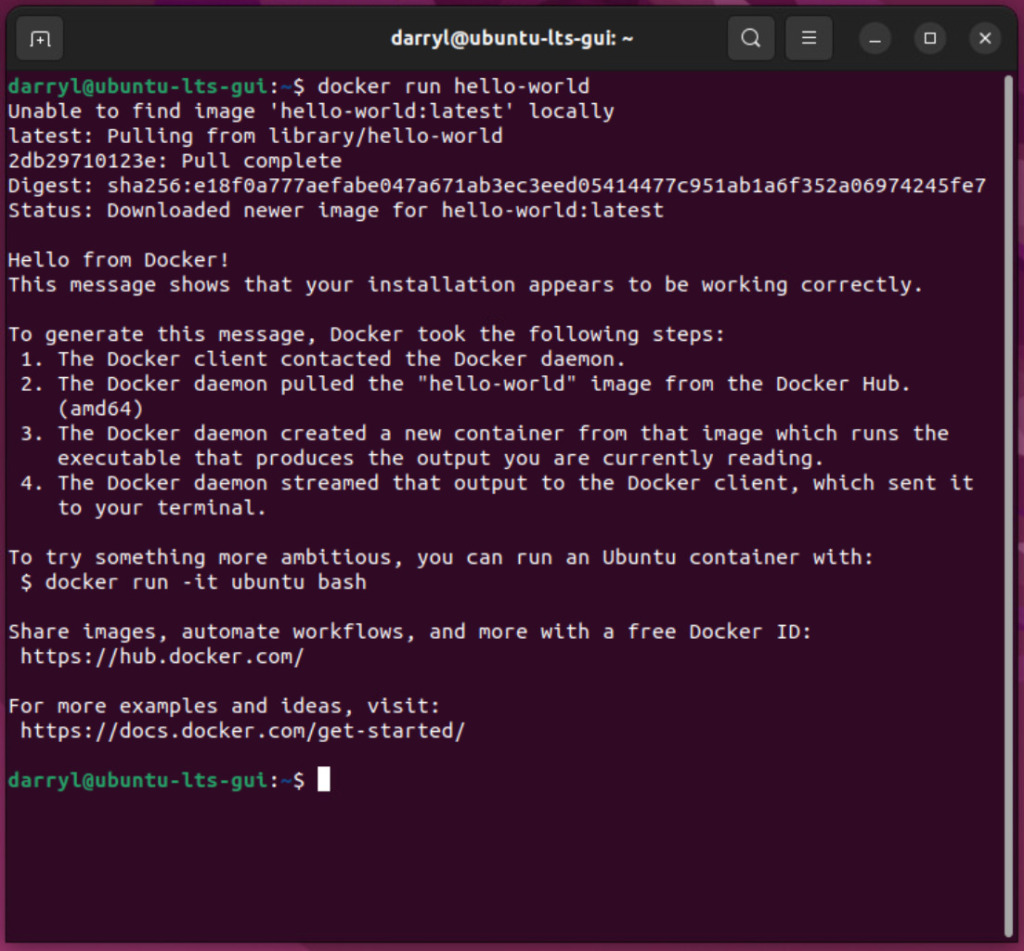
We have successfully got Docker up and running.
Leave a comment and share this article if you found it helpful.